What exactly are Xenobots? How could they help for a sustainable World?
Xenobots:
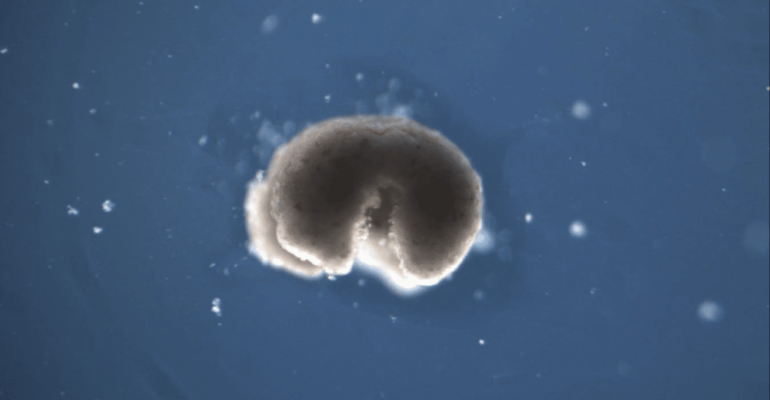
According to a study published in the scientific journal PNAS, Xenobots are the world’s first self-reproducing living robots.
They were initially presented in 2020 when studies discovered that they can move and join together. They are made from the stem cells of the African clawed frog.
Xenobots are “computer-designed organisms that gather single cells inside a Pac-Man-shaped “mouth”—and release Xenobot “babies” that look and move like themselves,” according to a video from Vermont University.
Who is Involved In The Research?
The research was developed by scientists from the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering.
According to scientists, Xenobots are a completely new kind of biological reproduction that is unlike any animal or plant now known to science.
“I was astouned by it,” Michael Levin, a professor of biology and director of Tufts University’s Allen Discovery Center, said of the study. Frogs have a way of reproducing that they normally utilize, but when you separate (the cells) from the rest of the embryo and give them an opportunity to figure out how to live in a new environment, they figure out not only a new way to move but also a new way to procreate.”
Josh Bongard, the study’s lead author and a computer science professor and robotics expert at the University of Vermont, elaborated on the Xenobots, saying:
“Most people think of robots as made of metals and ceramics but it’s not so much what a robot is made from but what it does, which is act on its own on behalf of people.
“In that way, it’s a robot but it’s also clearly an organism made from genetically unmodified frog cell.
Where Can I Learn More About The Study?
Follow the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and Harvard University on Twitter to learn more about the study.
Additionally, you can read the whole research from this publication here.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Q3eGk2g0Tk5DOXk1WnQuxjMh7qdi2baA/view
To more such interesting articles, follow absolinsoft.com